Trends
The Impact of Health Information Technology on Hospital Productivity in Saudi Arabia " A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis"
Assessment of Awareness Using Physiotherapy Devices at the Physical Therapy Center in Derna "A Field Awareness Study"
Awareness and Self-Use of Metronidazole for Diarrhea and Abdominal Pain Among Residents of Dongola City, Sudan
Background: Although Saudi Vision 2030 and the Health
Sector Transformation Program have made huge investments in health information
technology (HIT), there was no unified evidence on the effectiveness of HIT to
improve hospital productivity in the Saudi context.
Purpose: This study will be a systematic review and
meta-analysis of the effects of HIT implementation on hospital productivity
indicators in Saudi Arabia between 2018 and 2025.
Methods: In accordance with PRISMA 2020 criteria, we
have used PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science and regional databases. The inclusion
criteria included Saudi quantitative studies of hospitals that reported
efficiency, length of stay (LOS), throughput or financial performance following
HIT exposure. The meta-analysis used was random-effects meta-analysis; subgroup
analyses and meta-regression were conducted to evaluate the effects of hospital
type and HIT maturity.
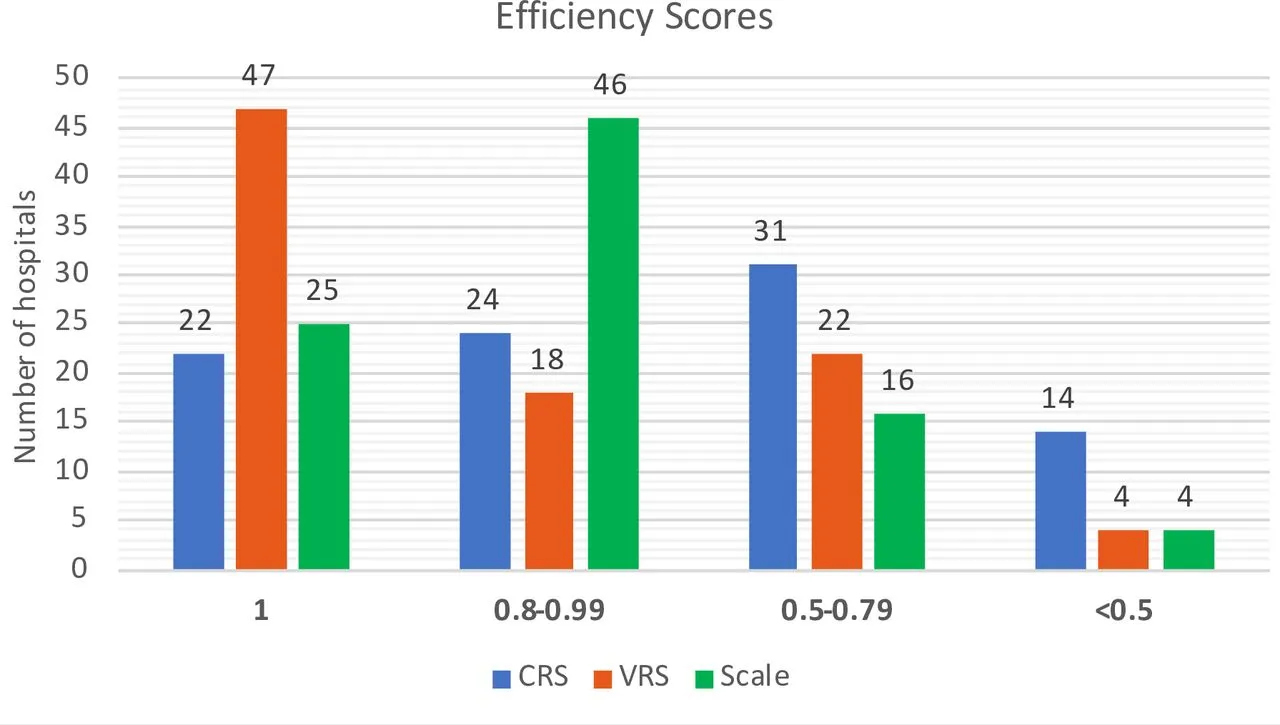
Findings: A total of 21 studies (428 unique hospitals
and 1.8 million discharges) were included; 12 of them were included in the
meta-analysis. Mature implementation of HIT was related to 18.4 percent
increased technical efficiency (SMD 0.62, 95% CI 0.41-0.83; p<0.001; 9
studies). 0.91-day decrease in the average LOS (WMD -.91 days, 95% CI -1.27 to
-.55; p=.000; 10 studies) 28.6% higher bed turnover rate (7 studies) 9.7%
reduction in the operational cost per case and 12.4% hike in the revenue per
bed (6 studies) The effects were significantly greater in public tertiary
hospitals and in those that had attained Stage 67 digital maturity (p=.000
Between-study heterogeneity was attributed to 64 percent to HIT maturity.
Conclusion: State-of-the-art, multifaceted HIT
demonstrates a significant level of correlation with significant productivity
improvements in Saudi hospitals, most significant of which are found in
large-volume tertiary hospitals. Smaller gains are realised in the private and
secondary facilities, most of which lack maturity and fragmented systems. These
results offer the initial solid arguments supporting a reason to invest further
in digital health at national levels and the implementation of performance-based
funding based on the milestones of digital maturity in the context of Vision
2030.

Hadi Hassan Mana Almakayil
Health AdministrationHadi Hassan Mana Almakayil Health Administration Technologist -Habuna general hospital hsalehhsaleh79@gmail.com Halmakayil@moh.gov.sa